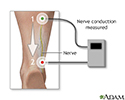
Nerve conduction velocity
NCV; Nerve conduction study (NCS)Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EMG) to assess the muscles for abnormalities.
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
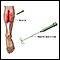
How the Test is Performed
Adhesive patches called surface electrodes are placed on the skin over nerves or muscles at different spots. A very mild electrical impulse is applied via other patches or a handheld stimulator to stimulate the nerve.
The resulting electrical activity of the nerve is recorded by the electrodes. The distance between electrodes and the time it takes for electrical impulses to travel between electrodes are used to measure the speed of the nerve signals. It is normal for several different nerves to be tested.
EMG is the recording from needles placed into the muscles. This is often done during the same visit as NCV.
How to Prepare for the Test
You must stay at a normal body temperature. Being too cold alters nerve conduction and can give false results.
Tell your health care provider if you have a cardiac defibrillator or pacemaker, or other implanted device such as a deep brain stimulator. Special steps may need to be taken before the test if you have one of these devices.
Do not wear any lotions, sunscreen, perfume, or moisturizer on your body on the day of the test.
How the Test will Feel
The impulse may feel like an electric shock. You may feel some discomfort depending on how strong the impulse is. You should feel no pain once the test is finished.
Often, the nerve conduction test is followed by EMG. In this test, a needle is placed into a muscle and you are told to contract that muscle. This process can be uncomfortable during the test. You may have muscle soreness or bruising after the test at the site where the needle was inserted.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is used to diagnose nerve damage or destruction. The test may sometimes be used to evaluate diseases of nerve or muscle, including:
- Myopathy
Myopathy
A muscle disorder causes patterns of weakness, loss of muscle tissue, electromyogram (EMG) findings, or biopsy results that suggest a muscle problem....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare disorder in which faulty communication between nerves and muscles leads to muscle weakness....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder. Neuromuscular disorders involve the muscles and the nerves that control them.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Carpal tunnel syndrome
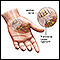
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which there is excessive pressure on the median nerve at the wrist. This is the nerve that allows feeling a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which the tibial nerve is being compressed. This is the nerve in the ankle that allows feeling and movement...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Diabetic neuropathy
- Bell palsy
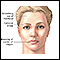
Bell palsy
Bell palsy is a disorder of the nerve that controls movement of the muscles in the face. This nerve is called the facial or seventh cranial nerve. D...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Guillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious health problem that occurs when the body's defense (immune) system mistakenly attacks part of the peripher...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brachial plexopathy
Brachial plexopathy
Brachial plexopathy is a form of peripheral neuropathy. It occurs when there is damage to the brachial plexus. This is a group of nerves that run f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ulnar nerve dysfunction
Normal Results
NCV is related to the diameter of the nerve and the degree of myelination (the presence of a myelin sheath on the nerve fiber) of the nerve. Newborn infants have values that are approximately half that of adults. Adult values are normally reached by age 3 or 4.
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Most often, abnormal results are due to nerve damage or destruction, including:
- Damage to the long portion of the nerve cell (axon degeneration or axonopathy)
- The impulse is blocked somewhere along the nerve pathway (conduction block)
- Damage and loss of the fatty insulation surrounding the nerve cell (demyelination)
The nerve damage or destruction may be due to many different conditions, including:
- Alcoholic neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy is damage to the nerves that results from excessive drinking of alcohol.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diabetic neuropathy
- Nerve effects of uremia (from kidney failure)
- Traumatic injury to a nerve
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious health problem that occurs when the body's defense (immune) system mistakenly attacks part of the peripher...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diphtheria
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an acute infection caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Brachial plexopathy
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (hereditary)
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a group of disorders passed down through families that affect the nerves outside the brain and spine. These are calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy
- Common peroneal/fibular nerve dysfunction
- Distal median nerve dysfunction
- Femoral nerve dysfunction
- Friedreich ataxia
Friedreich ataxia
Friedreich ataxia is a rare disease passed down through families (inherited). It affects the muscles and heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mononeuritis multiplex (multiple mononeuropathies)
Mononeuritis multiplex
Multiple mononeuropathy is a nervous system disorder that involves damage to at least two separate nerve areas. Neuropathy means damage to a periphe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radial nerve dysfunction
- Sciatic nerve dysfunction
- Secondary systemic amyloidosis
Secondary systemic amyloidosis
Secondary systemic amyloidosis is a disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensorimotor polyneuropathy
Sensorimotor polyneuropathy
Sensorimotor polyneuropathy is a condition that causes a decreased ability to move and feel (sensation) because of nerve damage.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tibial nerve dysfunction
- Ulnar nerve dysfunction
Any peripheral neuropathy can cause abnormal results. Damage to the spinal cord and disk herniation (herniated nucleus pulposus) with nerve root compression can also cause abnormal results.
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral nerves carry information to and from the brain. They also carry signals in both directions between the spinal cord and the rest of the bo...
Disk herniation
A herniated (slipped) disk occurs when all or part of a disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk. This may place pressure on nearby nerves...

Considerations
An NCV test shows the condition of the best surviving nerve fibers. Therefore, in some cases the results may be normal, even if there is nerve damage.
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC, Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 106.
Nuwer MR, Pouratian N. Monitoring of neural function: electromyography, nerve conduction, and evoked potentials. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 274.
Umansky D, Midha R. Peripheral nerve examination, evaluation, and biopsy. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 272.
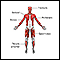
Nerve conduction test - illustration
The nerve conduction velocity test is performed to evaluate nerve function. It tests the speed impulses travel through a nerve.
Nerve conduction test
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.