CSF oligoclonal banding
Cerebrospinal fluid - immunofixationCSF oligoclonal banding is a test to look for inflammation-related proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is the clear fluid that flows in the space around the spinal cord and brain.
Oligoclonal bands are proteins called immunoglobulins. The presence of these proteins indicates inflammation of the central nervous system. The presence of oligoclonal bands may point to a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis.
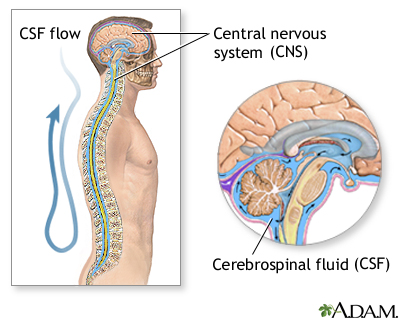
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Your brain and spinal cord serve as the main "processing center" for your entir...
How the Test is Performed
A sample of CSF is needed. A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common way to collect this sample.
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Other methods for collecting CSF are rarely used, but may be recommended in some cases. They include:
- Cisternal puncture
- Ventricular puncture
- Removal of CSF from a tube that is already in the CSF, such as a shunt or ventricular drain.
After the sample is taken, it is sent to a lab for testing.
Why the Test is Performed
This test helps support the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS). However, it does not confirm the diagnosis. Oligoclonal bands in the CSF may also be seen in other illnesses such as:
Multiple sclerosis
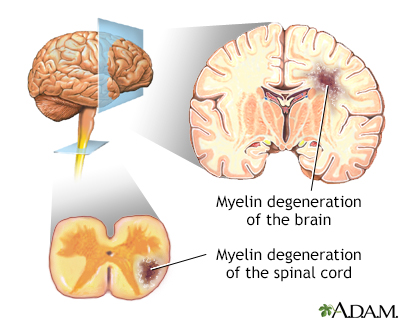
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections, such as Lyme disease and
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHuman immunodeficiency virus
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
One or no bands should be found in the CSF.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some labs use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
There are two or more bands found in the CSF and not in the blood. This may be a sign of multiple sclerosis or other diseases causing inflammation in the central nervous system.
References
De Luca GC, Griggs RC, Johnston SC. Approach to the patient with neurologic disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 366.
Karcher DS, McPherson RA. Cerebrospinal, synovial, serous body fluids, and alternative specimens. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 30.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Schnapp BH, Jewell C. Central nervous system infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 95.
CSF oligoclonal banding - series
Presentation
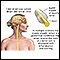
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
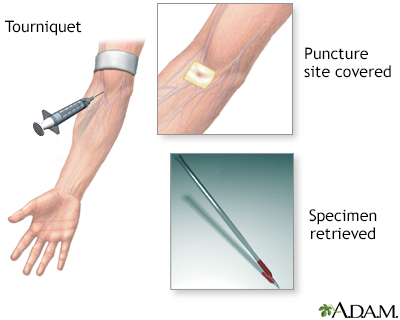
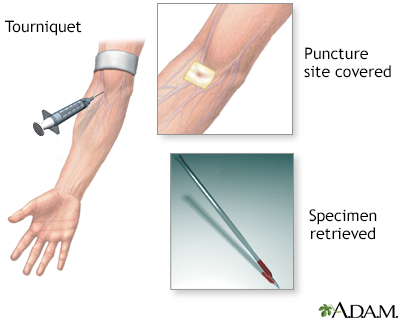
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
CSF oligoclonal banding - series
Presentation
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.