Aminoaciduria
Amino acids - urine; Urine amino acidsAminoaciduria is an abnormally high amount of amino acids in the urine. Amino acids are the building blocks for proteins in the body.
How the Test is Performed
A clean-catch urine sample may be needed. This is often done at your health care provider's office or health clinic.
Clean-catch urine sample
A clean catch is a method of collecting a urine sample to be tested. The clean-catch urine method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina ...
How to Prepare for the Test
Most of the time, you do not need to take special steps before this test. Make sure your provider knows all of the medicines you recently used. If this test is being done on an infant who is breastfeeding, make sure the provider knows what medicines the nursing mother is taking.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to measure amino acid levels in the urine. There are many different types of amino acids. It is common for some of each kind to be found in the urine. Increased levels of individual amino acids can be a sign of a problem with metabolism.
Normal Results
The specific value is measured in µmol/g creatinine. The values below represent normal ranges in 24 hours urine for adults. In children, normal values vary with age. In addition, normal values may vary between different laboratories. Talk to your provider about your specific test results.
Alanine: 78 to 1337
Arginine: 5 to 70
Asparagine: 25 to 454
Aspartic acid: 1 to 87
Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid is a nonessential amino acid. Amino acids are building blocks of proteins. "Nonessential" means that our bodies produce it, even if we...
Citrulline: 1 to 27
Cystine: 0 to 224
Glutamic acid: 5 to 92
Glutamine: 5 to 1756
Glycine: 277 to 7997
Histidine: 106 to 2534
Isoleucine: 5 to 48
Leucine: 5 to 129
Lysine: 15 to 1021
Methionine: 1 to 37
Ornithine: 5 to 76
Phenylalanine: 5 to 239
Proline: 5 to 169
Serine: 98 to 1053
Taurine: 24 to 5336
Threonine: 5 to 715
Tyrosine: 5 to 389
Valine: 5 to 147
The examples above show the common measurements for results for these tests. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Increased total urine amino acids may be due to:
- Alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is a rare condition in which a person's urine turns a dark brownish-black color when exposed to air. Alkaptonuria is part of a group of...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Canavan disease
Canavan disease
Canavan disease is a condition that affects how the body breaks down and uses aspartic acid.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Cystinosis
- Cystathioninuria
- Fructose intolerance
Hereditary fructose intolerance is a disorder in which a person lacks the protein needed to break down fructose. Fructose is a fruit sugar that natu...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleFructose intolerance
Hereditary fructose intolerance is a disorder in which a person lacks the protein needed to break down fructose. Fructose is a fruit sugar that natu...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Galactosemia
Galactosemia
Galactosemia is a condition in which the body is unable to use (metabolize) the simple sugar galactose.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hartnup disease
Hartnup disease
Hartnup disorder is a genetic condition in which there is a defect in the transport of certain amino acids (such as tryptophan and histidine) by the ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria is a genetic disorder that affects the metabolism of the amino acid methionine. Amino acids are the building blocks of all proteins i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hyperammonemia
- Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which 1 or more of the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a disorder in which the body cannot break down certain parts of proteins. The urine of people with this conditio...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Methylmalonic acidemia
Methylmalonic acidemia
Methylmalonic acidemia is a condition in which the body cannot break down certain proteins and fats. The result is a buildup of a substance called m...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
- Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones. It most often occurs because of a problem that leads to vitamin D deficiency, which helps your body absorb c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Propionic acidemia
- Rickets
Rickets
Rickets is a disorder that occurs in children before bone growth is complete. It is caused by a lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. It leads ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tyrosinemia type 1
- Tyrosinemia type 2
- Viral hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wilson disease
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Considerations
Screening infants for increased levels of amino acids can help detect problems with metabolism. Early treatment for these conditions may prevent complications in the future.
References
Dietzen DJ, Willrich MAV. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. In: Rifai N, Chiu RWK, Young I, Burnham Carey-Ann D, Wittwer CT, eds. Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 31.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Defects in metabolism of amino acids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 105.
Merritt JL, Gallagher RC. Inborn errors of carbohydrate, ammonia, amino acid, and organic acid metabolism. In: Gleason CA, Sawyer T, eds. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 29.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
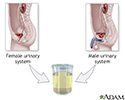
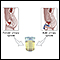
Urine sample - illustration
A clean-catch urine sample is performed by collecting the sample of urine in midstream. Men or boys should wipe clean the head of the penis. Women or girls need to wash the area between the lips of the vagina with soapy water and rinse well. A small amount of urine should initially fall into the toilet bowl before it is collected (this clears the urethra of contaminants). Then, in a clean container, catch about 1 to 2 ounces of urine and remove the container from the urine stream. The container is then given to the health care provider.
Urine sample
illustration
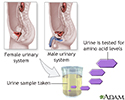
Aminoaciduria urine test - illustration
Aminoaciduria is a test that screens for increased levels of amino acid excretion in the urine which may indicate inborn errors of metabolism caused by a specific enzyme deficiency.
Aminoaciduria urine test
illustration
Urine sample - illustration
A clean-catch urine sample is performed by collecting the sample of urine in midstream. Men or boys should wipe clean the head of the penis. Women or girls need to wash the area between the lips of the vagina with soapy water and rinse well. A small amount of urine should initially fall into the toilet bowl before it is collected (this clears the urethra of contaminants). Then, in a clean container, catch about 1 to 2 ounces of urine and remove the container from the urine stream. The container is then given to the health care provider.
Urine sample
illustration
Aminoaciduria urine test - illustration
Aminoaciduria is a test that screens for increased levels of amino acid excretion in the urine which may indicate inborn errors of metabolism caused by a specific enzyme deficiency.
Aminoaciduria urine test
illustration
Review Date: 4/8/2025
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.