Kidney removal
Nephrectomy; Simple nephrectomy; Radical nephrectomy; Open nephrectomy; Laparoscopic nephrectomy; Partial nephrectomyKidney removal, or nephrectomy, is surgery to remove all or part of a kidney. It may involve:
- Part of one kidney removed (partial nephrectomy).
- All of one kidney removed (simple nephrectomy).
- Removal of one entire kidney, surrounding fat, and the adrenal gland (radical nephrectomy). In these cases, neighboring lymph nodes are sometimes removed.
Description
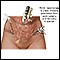
This surgery is done in the hospital while you are asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia). The procedure can take 3 or more hours.
Simple nephrectomy or open kidney removal:
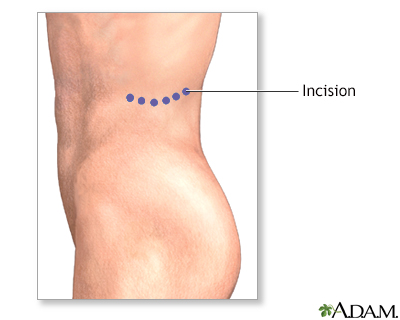
- You will be lying on your side. Your surgeon will make an incision (cut) up to 12 inches or 30 centimeters (cm) long. This cut will be on your side, just below the ribs or right over the lowest ribs.
- Muscle, fat, and tissue are cut and moved. Your surgeon may need to remove a rib to do the procedure.
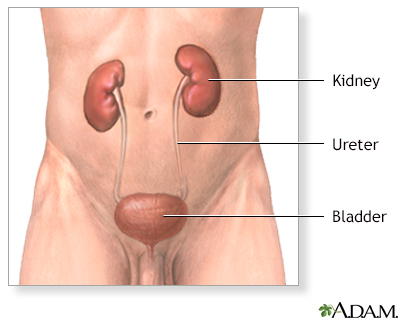
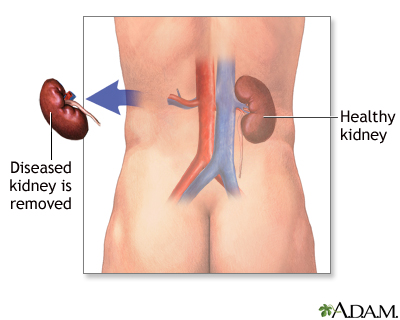
- The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder (ureter) and blood vessels are cut away from the kidney. The kidney is then removed.
- Sometimes, just a part of the kidney may be removed (partial nephrectomy).
- The cut is then closed with stitches or staples.
Radical nephrectomy or open kidney removal:
- Your surgeon will make a cut about 8 to 12 inches (20 to 30 cm) long. This cut will be on the front of your belly, just below your ribs. It may also be done through your side.
- Muscle, fat, and tissue are cut and moved. The tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder (ureter) and blood vessels are cut away from the kidney. The kidney is then removed.
- Your surgeon will also take out the surrounding fat, and sometimes the adrenal gland and some lymph nodes.
- The cut is then closed with stitches or staples.
Laparoscopic kidney removal:
- Your surgeon will make 3 or 4 small cuts, most often no more than 1 inch (2.5 cm) each, in your belly and side. The surgeon will use tiny probes and a camera to do the surgery.
- Towards the end of the procedure, your surgeon will make one of the cuts larger (about 4 inches or 10 cm) to take out the kidney.
- The surgeon will cut the ureter, place a bag around the kidney, and pull it through the larger cut.
- This surgery may take longer than an open kidney removal. However, most people recover faster and feel less pain after this type of surgery when compared to the pain and recovery period following open surgery.
Sometimes, your surgeon may make a cut in a different place than described above.
Some hospitals and medical centers are doing this surgery using robotic tools.
Surgery using robotic tools
Robotic surgery is a method to perform surgery using very small tools attached to a robotic arm. The surgeon controls the robotic arm with a compute...
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Kidney removal may be recommended for:
- Someone donating a kidney
- Birth defects
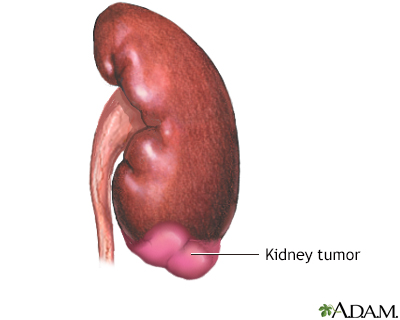
- Kidney cancer or suspected kidney cancer
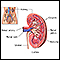
Kidney cancer
Renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer that starts in the lining of very small tubes (tubules) in the kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A kidney damaged by infection, kidney stones, or other problems
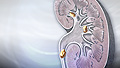
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - To help control high blood pressure in someone who has problems with the blood supply to their kidney
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Very bad injury (trauma) to the kidney that cannot be repaired
Risks
Risks of any surgery are:
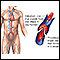
- Blood clots in the legs that may travel to the lungs
Blood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
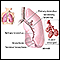
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing problems
Breathing problems
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection, including in the surgical wound, lungs (pneumonia), bladder, or kidney
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood loss
Blood loss
Bleeding is the loss of blood. Bleeding may be:Inside the body (internal)Outside the body (external)Bleeding may occur:Inside the body when blood le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack or stroke during surgery
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleStroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Reactions to medicines
Risks of this procedure are:
- Injury to other organs or structures
- Kidney failure in the remaining kidney
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - After one kidney is removed, your other kidney may not work as well for awhile
- Hernia of your surgical wound
Hernia
A hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Before the Procedure
Tell your surgeon or nurse if:
- You are or could be pregnant
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription
- You have been drinking a lot of alcohol, more than 1 or 2 drinks a day
Planning for your surgery:
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon may ask you to see the provider who treats you for these conditions.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If you smoke, it's important to cut back or quit. Smoking can slow healing and increase the risk for blood clots. Ask your provider for help quitting smoking.
Smoking can slow healing and increase t...
Quitting smoking and other nicotine products, including e-cigarettes, before surgery can improve your recovery and outcome after surgery. Most people...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleQuitting smoking
There are many ways to quit smoking. There are also resources to help you. Family members, friends, and co-workers may be supportive. But to be su...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If needed, prepare your home to make it easier to recover after surgery.
Prepare your home
Getting your home ready after you have been in the hospital often requires some preparation. Set up your home to make your life easier and safer when...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ask your surgeon if you need to arrange to have someone drive you home after your surgery.
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
- Let your surgeon know about any illness you may have before your surgery. This includes COVID-19, a cold, flu, fever, herpes breakout, or other illness. If you do get sick, your surgery may need to be postponed.
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCold
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFlu
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
On the day of the surgery:
- You will most often be asked not to drink or eat anything after midnight the night before the surgery.
- Take the medicines as you have been told, with a small sip of water.
- You will be told when to arrive at the hospital.
After the Procedure
You will stay in the hospital for 1 to 7 days, depending on the type of surgery you have. During a hospital stay, you may:
- Be asked to sit on the side of the bed and walk on the same day of your surgery
- Have a tube or catheter that comes from your bladder
- Have a drain that comes out through your surgical cut
- Not be able to eat the first 1 to 3 days, and then you will begin with liquids
- Be encouraged to do breathing exercises
- Wear special stockings, compression boots, or both to prevent blood clots
- Receive shots under your skin to prevent blood clots
- Receive pain medicine into your veins or pills
Recovering from open surgery may be painful because of where the surgical cut is located. Recovery after a laparoscopic procedure is most often quicker with less pain.
Laparoscopic
Pelvic laparoscopy is surgery to examine the pelvic organs. It uses a viewing tool called a laparoscope. The surgery is also used to treat certain ...
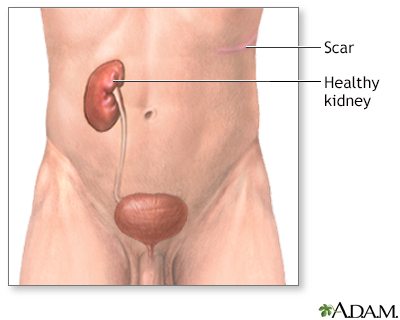
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is most often good when a single kidney is removed. If both kidneys are removed, or the remaining kidney does not work well enough, you will need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Kidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

References
Moreira DM, Kavoussi LR. Laparoscopic and robotic surgery of the kidney. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 102.
Olumi AF, Blute ML. Open surgery of the kidney. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 101.
Weiss RH, Jaimes EA, Hu SL. Kidney cancer. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 41.
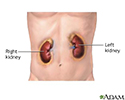
Kidneys - illustration
The kidneys are located in the posterior abdomen and are responsible for filtering urine from the blood.
Kidneys
illustration
Kidney removal (nephrectomy) - series
Presentation
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.