Secondary infections
A secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after treatment for another infection. It may be caused by the first treatment or by changes in the body or immune system that allow a second infection that is a secondary infection.
Two examples of a secondary infection are:
- A vaginal yeast infection after taking antibiotics to treat an infection caused by bacteria
Vaginal yeast infection
Vaginal yeast infection is an infection of the vagina. It is most often due to the fungus Candida albicans.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pneumonia caused by bacteria or fungi after having an upper respiratory infection (like a cold) that was caused by a virus
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a lung infection. It can be caused by many different germs, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This article discusses pneumonia th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Ison MG, Lee N. Influenza. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 332.
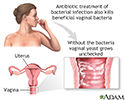
Secondary infection - illustration
Secondary infection occurs during or after treatment of a primary infection because the normal bacterial flora is destroyed, allowing yeast to flourish.
Secondary infection
illustration
Immune system structures - illustration
The immune system protects the body from potentially harmful substances. The inflammatory response (inflammation) is part of innate immunity. It occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat or any other cause.
Immune system structures
illustration
Secondary infection - illustration
Secondary infection occurs during or after treatment of a primary infection because the normal bacterial flora is destroyed, allowing yeast to flourish.
Secondary infection
illustration
Immune system structures - illustration
The immune system protects the body from potentially harmful substances. The inflammatory response (inflammation) is part of innate immunity. It occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat or any other cause.
Immune system structures
illustration
Review Date: 8/5/2025
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
© 1997- A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.