Empty sella syndrome
Pituitary - empty sella syndrome; Partial empty sellaEmpty sella syndrome is a condition in which the pituitary gland shrinks or becomes flattened.
Causes
The pituitary is a small gland located just underneath the brain. It is attached to the bottom of the brain by the pituitary stalk. The pituitary sits protected inside a saddle-like bony compartment in the base of the skull. This compartment is called the sella turcica, but often just called the sella.
When the pituitary gland shrinks or becomes flattened, it cannot be seen on an MRI scan. This makes the area of the pituitary gland look like an empty sella. But the sella is not actually empty. It is often filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. With empty sella syndrome, CSF has leaked into the sella turcica, putting pressure on the pituitary. This causes the gland to shrink or flatten.
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
Primary empty sella syndrome occurs when one of the layers (arachnoid) covering the outside of the brain bulges down into the sella and presses on the pituitary.
Secondary empty sella syndrome occurs when the sella is empty because the pituitary gland has been damaged by:
- A tumor
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Surgery
- Trauma
Empty sella syndrome may be seen in a condition called pseudotumor cerebri, which mainly affects young, obese women and causes the CSF to be under higher pressure.
Pseudotumor cerebri
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a condition in which the pressure inside the skull is increased. The brain is affected in a way that t...
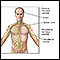
The pituitary gland makes several hormones that regulate other glands and hormones in the body, including:
- Adrenal glands
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are two small triangle-shaped glands in the upper abdomen. One gland is located on top of each kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver hormone related to growth (insulin-like growth factor-1)
- Ovaries
- Testicles
- Thyroid
A problem with the pituitary gland can lead to problems with any of the above glands and abnormal hormone levels of these glands.
Symptoms
Often, there are no symptoms or loss of pituitary function.
If there are symptoms, they may include any of the following:
- Erection problems
Erection problems
An erection problem occurs when a man cannot get or keep an erection that is firm enough for intercourse. You may not be able to get an erection at ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headaches
- Irregular or absent menstruation
- Decreased or no desire for sex (low libido)
- Fatigue, low energy
- Nipple discharge
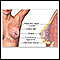
Nipple discharge
Nipple discharge is any fluid that comes out of the nipple area in your breast.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Primary empty sella syndrome is most often discovered during an MRI or CT scan of the head and brain. Pituitary function is usually normal.
MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.

Your health care provider may order tests to check if the pituitary gland is working normally.
Sometimes, tests for high pressure in the brain will be done, such as:
- Examination of the retina by an ophthalmologist
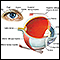
Examination of the retina
Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the back part of the eye (fundus), which includes the retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
For primary empty sella syndrome:
- No treatment is needed if pituitary function is normal.
- Medicines may be prescribed to treat any abnormal hormone levels.
For secondary empty sella syndrome, treatment involves replacing the hormones that are missing.
In some cases, surgery is needed to repair the sella to prevent CSF from leaking into the nose and sinuses.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Primary empty sella syndrome does not cause health problems, and it does not affect life expectancy.
Possible Complications
Complications of primary empty sella syndrome include a slightly higher than normal level of prolactin. This is a hormone made by the pituitary gland. Prolactin stimulates breast development and milk production in women.
Complications of secondary empty sella syndrome are related to the cause of pituitary gland disease or to the effects of too little pituitary hormone (hypopituitarism).
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a condition in which the pituitary gland does not produce normal amounts of some or all of its hormones.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of abnormal pituitary function, such as menstrual cycle problems or impotence.
References
Bashari WA, Gillett D, MacFarlane J, Scoffings D, Gurnell M. Pituitary imaging. In: Melmed S, ed. The Pituitary. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Johannsson G, Ragnarsson O. Hypopituitarism including growth hormone deficiency. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 5.
Kaiser U, Ho KKY. Pituitary physiology and diagnostic evaluation. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 6.
Weiss RE. Anterior pituitary. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 205.
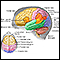
The pituitary gland - illustration
The pituitary is a gland attached to the base of the brain. The pituitary secretes hormones that regulate the body's balance of many hormones controlling growth, development, and metabolism of the body.
The pituitary gland
illustration
Review Date: 4/24/2025
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.